The  elements of healthy ageing
elements of healthy ageing
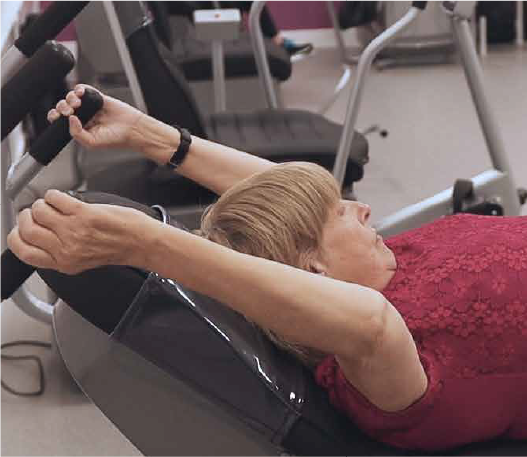
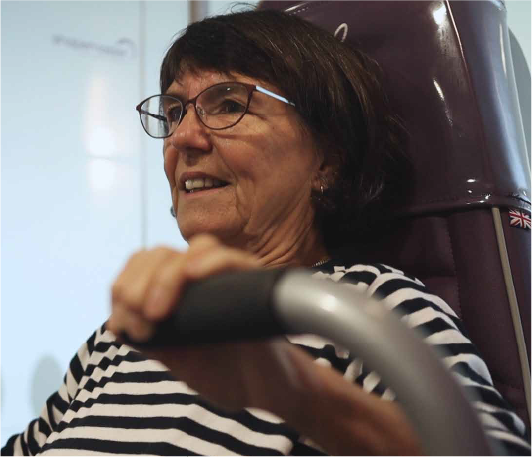
The components of fitness and physical performance which are central to sustained wellbeing amongst older adults are aerobic fitness, muscular strength, balance, flexibility and social wellbeing. With age, we lose muscle tissue and our muscles become more rigid and less toned, and alongside this, older adults also see a deterioration in balance. Aerobic exercise, strength training and stretching help to maintain and improve strength, cardiovascular health and flexibility and help to counter this natural process, thereby improving quality of life for older adults.
Innerva's range of equipment has been evaluated in numerous studies over the years, most recently in late 2021, at the AWRC (Advanced Wellness Research Centre) based at Sheffield Hallam University, where biomechanical, muscular and physiological responses to power assisted exercise amongst healthy older adults were measured. Results conclusively showed the immediate beneficial physical responses to exercising on Innerva equipment and hence the positive impact on the five elements of healthy ageing, assisting in maintaining and improving the quality of everyday living.
The most recent study results showed that users of Innerva equipment achieved an average metabolic equivalent of 3-4 METS across a range of Innerva machines during their workout including an initial warm up, through to their main workout and cooldown. In fact, participants achieved up to 8 to 9 METS at some points, with some achieving maximal heart rates (for their age) of up to 130/140 bpm. The interval nature of the Innerva workout allows users to work from low to moderate to high intensity exercise, with harder efforts being equivalent to jogging at a moderate pace or taking part in a vigorous game of tennis! This data is strong evidence that exercising with Innerva equipment will improve aerobic fitness.